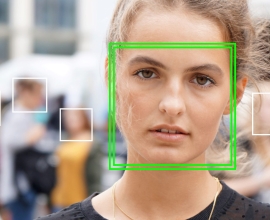
Facial recognition systems have spread ubiquitously across modern life. Once a futuristic technology, face detection systems have grown into an essential tool for many contemporary industries including advertising, security and social media. Fuelled by the rapid rise in big data, deep neural networks and extremely powerful GPUs, facial recognition offers unparalleled security and personalization opportunities.
What is facial recognition?
Facial recognition is the biometric technology used to identify or confirm an individual’s identity using their face. Such systems use biometrics to analyze facial features from a photograph, video or real-time livestream to compare the incoming face to a dataset of trained images.
How does facial recognition work?
Biometrics are captured, mapped, analyzed and then confirm the identity of a face compared against a specific database of faces. Depending on the specification of the camera device and facial recognition system, the incoming image of the face can either be captured in two-dimensions or three-dimensions.
The faces are analyzed according to geometry of their facial features, including but not limited to:
- Spacing and distance between the eyes
- Bridge and shape of the nose
- Contour of the chin, ears and lips
The more advanced facial recognition systems are able to detect faces at various angles, as well as detecting multiple faces within a photo, video or livestream simultaneously. In addition to matching faces to those within a database, this facial recognition attribute determination can be applied to ascertain the age, gender and / or emotions of those within a photograph.
What factors influence the accuracy of facial recognition systems?
The accuracy of these systems is determined by a combination of multiple factors. The quality of face image supplied during both the dataset training stage and the live identification stage will heavily influence the accuracy rate of the facial recognition system. When training this type of system, it is highly recommended that several photos of the same person, from multiple different angles and under different lighting conditions, are added to the training dataset so that a higher quality of image recognition can be achieved. The more information provided to a dataset, the more accurate the prediction.
Other determinant factors include:
- Face posture
- Facial expression
- Glasses
- Makeup
- Hair and facial hair
Where is facial recognition used?
Face detection systems can be split into three primary categories; Face Detection, Face Recognition and Face Grouping. These systems have use cases across a wide variety of industries. Here is our selection of the top five applications of facial recognition:
-
Personalized advertising campaigns
Using meta information such as gender, age or emotions, the attributes detection aspect of facial recognition can be used to tailor and personalize advertisements to the viewer. Rather than mass market blanket advertising, facial recognition offers scalable cloud based on-demand personalization for advertisers using billboards or digital displays to show specific adverts to people based on certain characteristics. This level of personalization helps to improve the efficiency and cost effectiveness of advertising by ensuring that the adverts are not wasted on irrelevant people who do not fit the advertiser’s target audience.
-
Time attendance and user authentication
Many people will have experienced using their phone, tablet or computer camera to register their face. Often used for the purpose of unlocking a device for the specific user, this type of facial recognition has widespread uses for time and attendance systems that help to accurately record and measure work patterns and shifts from employees. By using this innovative software, companies are able to eliminate buddy punching and can speed up the clocking in and out process as the facial recognition allows for passive recognition, rather than requiring the staff to actively log their attendance.
-
Social media profile moderation and verification
Online security and content moderation is a key concern for contemporary social media platforms. Profile verification is one of the ways being explored to reduce trolling, spamming and fraudulent activity online. Historically, profile verification was a tedious manual process that was highly susceptible to human error. Using facial detection and other associated deep learning systems, profile verification has become a quick yet robust process that helps to eliminate fakes and forgeries.
Just like social media applications, other apps may choose to integrate facial recognition technology as a wall of security or part of the application itself. With more app design and development agencies, such as Ronins, improving year on year with the level of app software made available to the consumer market, it is exciting to see how it all continues to evolve overtime!
-
Law enforcement
Mugshots have long been part of the police’s arsenal for identifying and tracking down suspects or convicts. Once an arrested individual has their photograph taken, this will be added to the police facial recognition database, to be scanned whenever the police carry out another criminal search. Often used in conjunction with crime scene footage recovered from closed circuit television, the ability for advanced person detection systems to identify a face from multiple angles and across a wide variety of lighting conditions has proved invaluable to police forces across the world when searching for a suspect from grainy or dark footage.
-
Reducing online banking fraud
Security is paramount for online banking, especially when involving transferring funds or approving purchases. By integrating biometric identification into online banking, bank providers can use biometrics to remove the risk of passwords being compromised or one-time passwords being intercepted. Even if the hackers are able to get hold of a photo database, the liveness detection built into most facial recognition systems will prevent any fake representations of a person being used to fraudulently access a bank account.
Whilst facial recognition is often used in association with other forms of biometric authentication such as voice recognition, fingerprint recognition or iris recognition, it is often the most passive system involving the least effort from the individual. This enables great scalability, especially for large, fast moving crowds. In most situations, the only hardware required is a camera unlike other systems such as fingerprint identification which require specialist fingerprint scanners.
Overall, facial recognition systems offer very compelling security and personalisation solutions. Whilst there are persistent concerns surrounding nefarious uses of these systems, the convenience and accuracy of facial recognition means the adoption of the biometric technology will remain widespread across a range of industries and applications.